Have you ever wondered what happens when you stop using Rogaine?
If you're considering a break from this popular hair regrowth treatment, you're not alone. Many are curious about the effects of discontinuing Rogaine.
In this article, we'll explore the potential changes and provide tips to maintain your hair health during the transition.
Stick around to the end and we'll reveal what made Niels hair transformation possible.
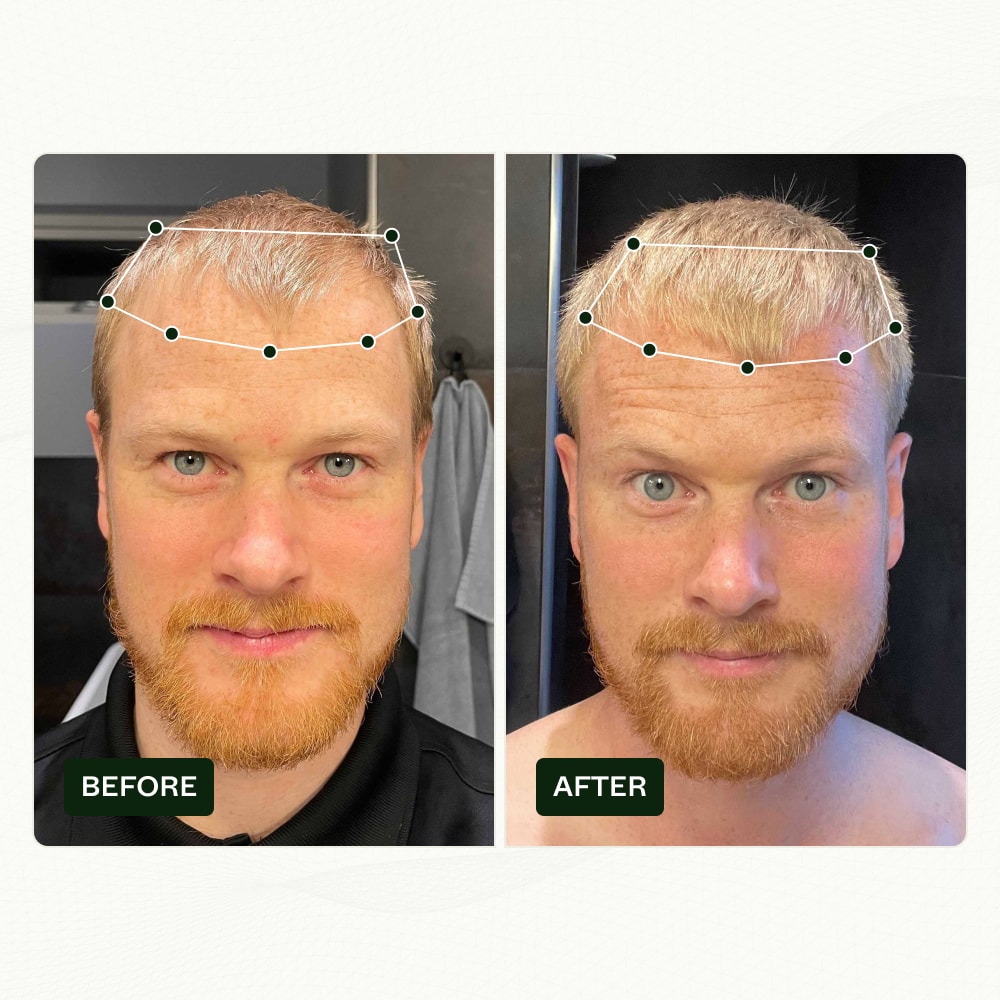

Table of content
As your leading source for hair health information over the past 4 years, we never compromise on accuracy. When it comes to your health, you deserve information you can truly rely on - and earning your trust is our top priority.
Here's how Scandinavian Biolabs ensures every piece of content meets the highest standards of accuracy and integrity:
- Credentialed Experts: Our reviewers are actively practicing doctors and medical researchers
- Stringent Reviews: Content undergoes rigorous editing by subject specialists and review by a practicing doctor.
- Evidence-Based: We rely on well-established research from trusted scientific sources like peer-reviewed journals and health authorities.
- Full Transparency: Our editorial standards, writer credentials, reviewer credentials, correction process, and funding are all publicly documented.
- Independent Voice: While we do promote products, we operate in a vacuum to business operations. Our main goal is just an unwavering commitment to providing medically-sound guidance.
You can count on Scandinavian Biolabs to consistently deliver the trustworthy health information you deserve. Read our Editorial Standards.
How does Rogaine work?
Rogaine works by widening blood vessels and opening potassium channels in the hair follicles, promoting hair growth.
When applied, Rogaine is absorbed by the skin and converted by the enzyme sulfotransferase into its active form, minoxidil sulfate.
This active form causes vasodilation, which improves blood flow to the hair follicles, delivering more nutrients and oxygen.
The increased circulation supports cell metabolism and encourages the proliferation of cells within the hair follicles, leading to healthier hair growth and combating pattern baldness.
What happens when you stop using Rogaine?
When you stop using Rogaine, new hair growth stimulated by the medication will be lost, and your scalp will gradually return to its pre-treatment condition. Hair regrowth slows or stops, existing regrown hair may fall out, and hair loss usually reverts to its original state.
Consult a healthcare professional before stopping to understand the best course of action for your hair health.
Why might you stop using Rogaine?
There are several reasons people might decide to stop using Rogaine:
- Lack of expected hair growth results.
- Experiencing significant side effects.
- The daily cost of using Rogaine becomes too high.
- Concerns about interactions with other medications.
- Achieving desired results and no longer needing the treatment.
Typically, people are more likely to discontinue Rogaine if they don't see noticeable improvements or if they suffer from adverse effects.
How does Rogaine affect the hair growth cycle?
Rogaine stimulates existing hair follicles to remain active for a longer duration in the growth-promoting anagen phase.
It also signals more resting follicles to restart the growth cycle earlier by shortening the inactive telogen rest phase.
Both actions prolong the cycle and increase the number of new hair shafts produced per follicle, leading to thicker hair coverage.
This cascade effect takes months to manifest but explains how Rogaine promotes new hair growth over prolonged use.

Anagen phase
During the anagen phase, the hair follicle is actively growing the hair shaft. This phase typically lasts 2-6 years for scalp hair. Rogaine stimulates follicles in the anagen phase to grow hair for a longer duration.
It does this by opening potassium channels in the dermal papilla cells at the base of the follicle. This increased potassium level stimulates cellular activity and signals the follicle to remain in the growth-active anagen phase.
Catagen phase
Once the anagen phase ends naturally, the hair enters a brief transitional or regressive phase called catagen.
This phase signals the follicle to stop hair production and transitions it to rest. Rogaine has no significant effect during catagen.
Telogen phase
The resting telogen phase usually lasts around 3 months. During this time, the hair shaft is not growing. Rogaine works by shortening this telogen phase.
It causes more resting follicles to prematurely re-enter the anagen growth phase. This induces more follicles to produce hair simultaneously, resulting in increased hair density over time with continuous use.
How long do minoxidil side effects last after stopping?
Most minoxidil side effects end within 2 weeks, and hair loss returns within 6 months. But some unpleasant side effects can persist if you're unlucky:
- Headaches, dizziness, fatigue, swelling, and tenderness don't always disappear so quickly for everyone. If you're one of the unfortunate ones, these symptoms could plague you for over a month after stopping.
- Unwanted hair growth (think beard hair, body hair) is a common long-term issue - minoxidil has a way of stimulating dormant follicles that may never return to sleep.
- Changes in existing hair aren't always fleeting either. Thinning hair, shedding, and odd textures can last 6 months or more even after you quit. Your hair may never fully recover normalcy.
- Irritated and dry flaky skin may persist irritatingly for the long haul. Some sufferers battle dermatitis-like issues for years because of minoxidil.
- Chest pain, palpitations or changes in blood pressure could indicate more severe cardiovascular side effects that linger.
Read more: How long do minoxidil side effects last after stopping?
Will you lose more hair if you stop using minoxidil?
Yes, stopping Minoxidil often leads to resumed hair loss, with some people losing more hair than they had before starting treatment. This can vary widely from person to person.
When you stop using Minoxidil, hair loss typically resumes because the medication's effects are no longer active.
A study found that 40% of men had hair counts below baseline levels after discontinuing Minoxidil. This means that it's possible to lose more hair than you initially regrew.
Hair loss conditions like male pattern baldness and female pattern hair loss are progressive, meaning they worsen over time without treatment.
Therefore, it's crucial to address hair loss early if it's a concern for you, as continuous treatment may help maintain hair growth and prevent further loss.
How to treat minoxidil side effects after stopping?
To treat minoxidil side effects after stopping use, allow your body time to adjust as it clears the drug from your system. Drink plenty of water and get enough rest. Over-the-counter remedies like ibuprofen can help relieve headaches. Most side effects are temporary and should subside within a few weeks.
When you stop using minoxidil, your body needs to readjust after being dependent on it. Common withdrawal side effects include headaches, dizziness, itching, and shedding of hair.
- Staying well hydrated helps flush the drug from your system faster.
- Getting enough sleep also aids your body's recovery.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help with headaches.
- Minor skin irritation may be soothed with moisturizer.
While uncomfortable, most side effects are mild and temporary, subsiding within 1-4 weeks as minoxidil leaves your system. See a doctor if symptoms are severe or last longer than this.
How long does it take for minoxidil to exit your body?
Minoxidil is cleared from the body fairly quickly. Most of the minoxidil dose is metabolized in the liver and excreted within a day through urine and feces. However, the effects of minoxidil on hair regrowth may last up to 2-3 months after stopping treatment as hair follicles remain in the growing phase longer.
While minoxidil is cleared from the body within about 24 hours, its effects don't immediately disappear after stopping use.
That's because it can take hair follicles 2-3 months to complete the growth phase induced by minoxidil and then return to their normal growth cycle.
During this time, users may still see some hair regrowth benefits even after the drug has long since left their system.
This residual effect is why experts recommend continuing minoxidil for at least 4-6 months to fully evaluate its hair loss treatment potential before considering alternative options.
What happens if you stop minoxidil and start again?
Restarting Minoxidil after a break can help you regain the hair you've lost since stopping, with the same potential for effectiveness as before. However, you may also experience the same side effects and possibly another phase of Minoxidil shedding.
If Minoxidil worked for you initially, there's a good chance it will work again upon restarting.
Be aware that the side effects you experienced before are likely to return unless you switch to a lower strength or reduce the frequency of application.
Additionally, depending on how long it’s been since you last used Minoxidil, you might go through a shedding phase again. If your break was short (less than two or three months), you might avoid this shedding phase.
However, if it’s been longer than a few months, expect some additional shedding as your scalp readjusts to the treatment.
Should you stop using Rogaine?
You may want to stop using Rogaine if you are not seeing any hair growth results after several months of use. Rogaine can cause unwanted side effects like skin irritation for some users and more severe side effects in some cases.
Rogaine, or minoxidil, is generally considered safe when used as directed. And the minoxidil shedding within the first few months of use are normal and well-documented.
However, if after consistent use over several months little hair regrowth is seen, or side effects occur, it's reasonable to discuss other options.
They can help evaluate if a different treatment may be more effective based on your hair loss type and genetics.
How do you stop minoxidil without losing hair?
To prevent hair loss when stopping minoxidil, taper usage gradually over several months. Slowly reduce application frequency to allow hair follicles time to readjust.
For example, apply it every other day for 1 month then 2-3 times per week for another month before quitting. This gradual approach lessens the chance of shock losing regained hair.
Tapering minoxidil use slowly over a few months is key to minimizing potential hair shedding when stopping treatment.
Going cold turkey can shock hair follicles that had become dependent on its stimulating effects. By gradually spacing out applications, it gives hair time to readapt to normal growth cycles on its own without the drug's influence.
Reducing to every other day, then a few times a week allows hair to wean off minoxidil exposure and helps retain hair gained during treatment.
During this time, you can consider using alternative hair growth products like hair growth serums, caffeine shampoo, essential oils, derma rolling, etc.
What's the best minoxidil alternative with no harmful side effects?

One option is Bio-Pilixin, a formula that takes a multi-pronged approach to hair growth support. Rather than relying on a single active ingredient, Bio-Pilixin incorporates several research-backed components.
Biotin is included to strengthen hair follicles, while caffeine has been shown in studies to stimulate dormant follicles. Other plant extracts aim to provide important nutrients to the scalp.
Where some products focus only on circulation or stimulation alone, Bio-Pilixin addresses various stages of the growth cycle. It aims to nourish the scalp environment and support existing hair from within.
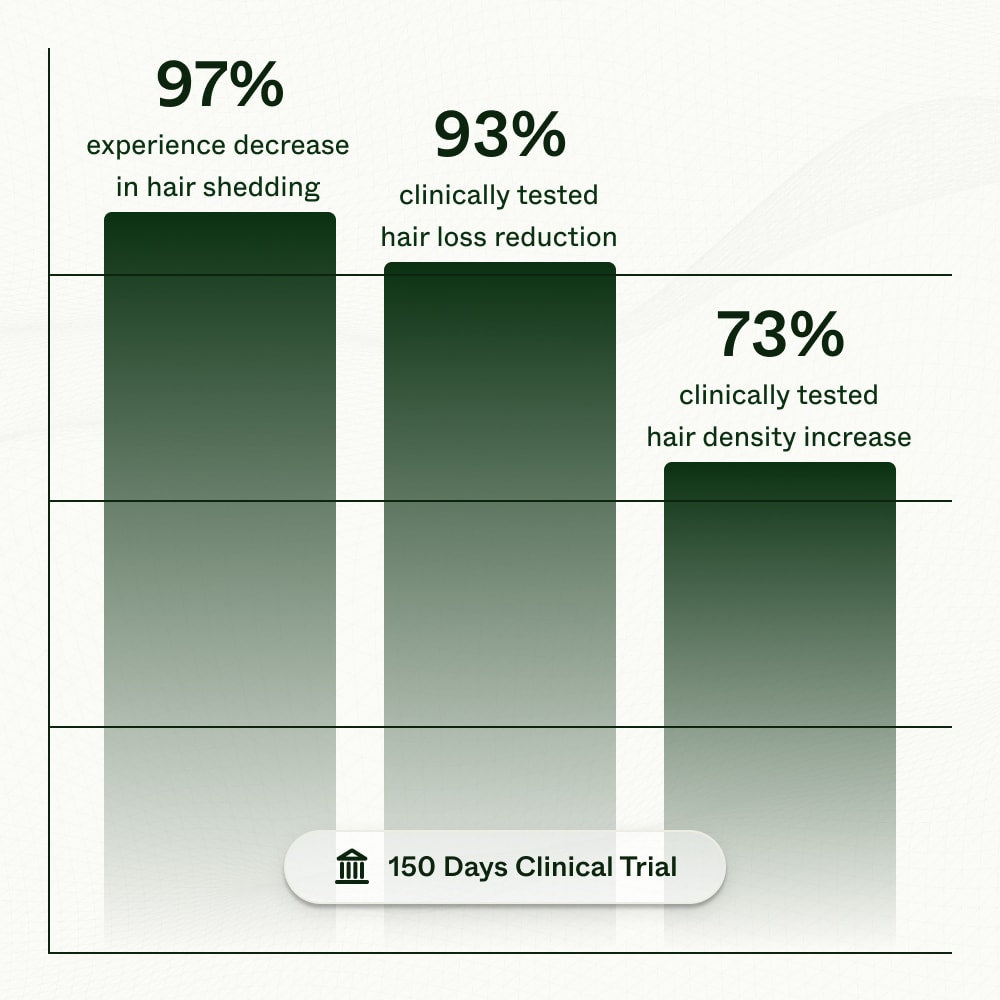
A clinical trial was conducted evaluating Bio-Pilixin's effects over 150 days. Key findings reported by researchers included:
- Over 90% of participants saw a reduction in hair shedding, averaging around 45% less shedding. One participant had an 85% reduction.
- Over 70% of participants experienced increased hair density, with some seeing up to a 23% gain.
- Hair in the growth phase increased by 17.5% while hair in the rest phase decreased by 36.5%.
- 80% reported moderate to strong hair loss reduction effects.
- Over 90% were satisfied with results in reducing hair loss.
Notably, Bio-Pilixin's formula is free of unnecessary ingredients like parabens and sulfates that could potentially irritate the scalp long-term.
This clean approach may support more sustainable results over time compared to other treatments.
While no single product is right for everyone, Bio-Pilixin's holistic system and research into optimized dosing of ingredients make it a strong potential alternative for those seeking an option without minoxidil.
Our money-back guarantee allows trying it firsthand to see results without a big investment.
Conclusion
Suffering from androgenetic alopecia or alopecia areata is a problem many people face.
But you don't have to put your life experience at risk over some hair fall.
Stopping Rogaine can result in returning female and male pattern baldness since minoxidil requires consistent use to be effective.
However, it's understandable that you might be worried about their side effects on your body.
There are alternatives with no harmful side effects available for those who seek to regrow hair.
It's also worth consulting with a professional about whether topical finasteride, hair transplant surgery, or oral minoxidil might be a better option for you.
If your family has a history of breast cancer or skin cancer, consult a hair loss professional before starting.
Here's to hoping you'll never have to experience permanent hair loss.






