Did you know the health of your teeth might affect your luscious locks? Yes, you heard that right! A tooth infection isn't just about pain and discomfort; it can surprisingly lead to hair loss.
In this easy-to-understand guide, we're exploring how a problem in your mouth could lead to thinning hair.
We have all the necessary information, from understanding the connection to finding solutions. Let's unravel this mystery and discover how to keep your smile, eyebrows, and facial hair both in top-notch condition!
Table of content
Can a tooth infection cause hair loss?
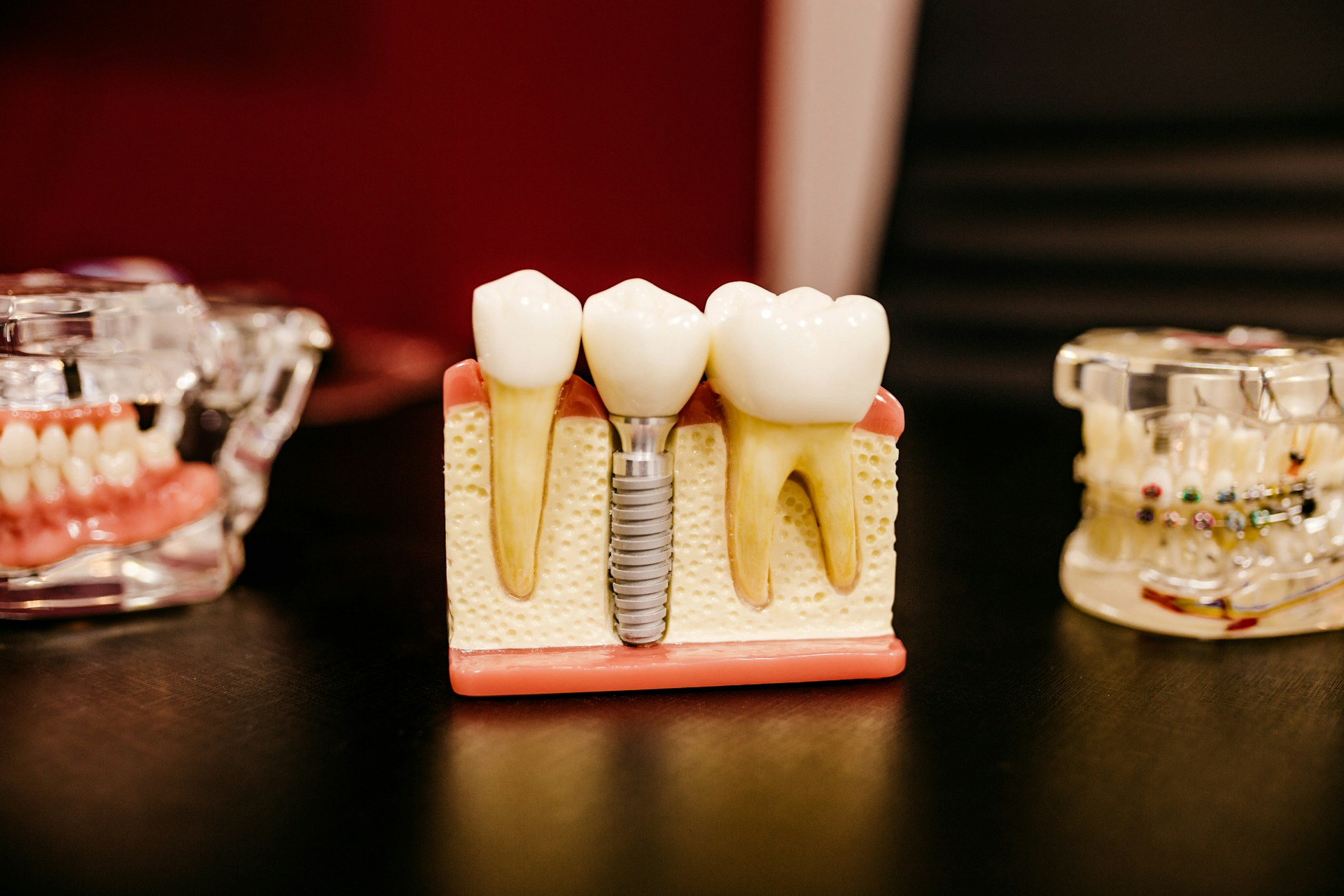
Yes, a tooth infection can potentially lead to hair loss indirectly. This occurs when the infection causes systemic inflammation or spreads bacteria throughout the body, which can disrupt hair follicles and growth cycles. Such disruptions can trigger conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase.
Furthermore, severe infections might lead to nutritional deficiencies or stress, also known to affect hair health.
While not a common cause, addressing tooth infections promptly is crucial to avoid any possible impact on overall health, including hair loss. Maintaining good dental hygiene and seeking timely treatment for dental issues can help minimize this risk.
As your leading source for hair health information over the past 4 years, we never compromise on accuracy. When it comes to your health, you deserve information you can truly rely on - and earning your trust is our top priority.
Here's how Scandinavian Biolabs ensures every piece of content meets the highest standards of accuracy and integrity:
- Credentialed Experts: Our reviewers are actively practicing doctors and medical researchers
- Stringent Reviews: Content undergoes rigorous editing by subject specialists and review by a practicing doctor.
- Evidence-Based: We rely on well-established research from trusted scientific sources like peer-reviewed journals and health authorities.
- Full Transparency: Our editorial standards, writer credentials, reviewer credentials, correction process, and funding are all publicly documented.
- Independent Voice: While we do promote products, we operate in a vacuum to business operations. Our main goal is just an unwavering commitment to providing medically-sound guidance.
You can count on Scandinavian Biolabs to consistently deliver the trustworthy health information you deserve. Read our Editorial Standards.
The connection between alopecia areata and tooth infection

The connection between alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, and tooth infection lies in the body's immune response. A tooth infection can trigger an excessive immune response, potentially leading to misdirected attacks on hair follicles nearby cells, thus leading to a sudden patchy hair loss and a weaker immune system.
This autoimmune activity can exacerbate or trigger alopecia areata in susceptible individuals.
Research suggests that dental infections, especially those causing chronic inflammation, may influence autoimmune diseases by altering the body's immune regulation.
While not directly causing alopecia areata, tooth infections could worsen or precipitate its onset in predisposed persons.
Addressing dental health issues promptly and maintaining good oral hygiene may reduce the risk of such complications. It highlights the importance of comprehensive healthcare, recognizing the interconnectedness of oral health and systemic conditions.
Signs your tooth infection has spread
When a tooth infection spreads, it can lead to more severe symptoms beyond the initial pain and discomfort. Recognizing these signs early stages is crucial for timely treatment:
Swelling in the face or cheek
This occurs as the infection moves out of the tooth's root and into surrounding tissues and cells, causing noticeable puffiness or swelling on one side of the face. It's a sign that the body is fighting the infection but also indicates its escalation.
Increased pain, sometimes radiating to the jaw, neck, or ear
As the infection spreads, the area of discomfort widens. Pain is no longer confined to the root canal or tooth; depending on both the infection's location and severity, it can radiate towards the jawbone, neck, and even the ear.
Fever or high temperature
Fever is a common systemic response to dental infection. A high temperature when you have a tooth infection suggests your body is attempting to fight off both the infection and widespread disease.
A general feeling of unwellness or malaise
Feeling generally unwell, tired, or lethargic can of course accompany the spread of an infection as your body expends energy to combat the invading bacteria.
Difficulty swallowing or breathing
When the infection spreads to the throat or the respiratory tract, it can swell, making it hard to swallow or breathe. This is an alarming sign that requires immediate medical intervention.
Pus or discharge from around the infected tooth
The presence of pus or a discharge is a direct sign of infection. It indicates that the body is trying to expel the bacteria causing the infection.
Swollen lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck
The lymph nodes act as filters for foreign particles in white blood cells and are part of the immune system. When they're swollen, it's a response to infection in the affected area of the body, indicating that the disease might be spreading or becoming more serious.
These symptoms suggest that what started as a localized dental issue is now affecting broader areas and potentially leading to more significant health concerns. Immediate medical and dental care is crucial to manage the infection and prevent further health risks.
How to prevent a tooth infection?
Preventing tooth infections involves maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Key practices include brushing teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco. Regular dental visits for cleanings and exams can catch potential issues early before they develop into infections.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brushing your teeth at least twice daily and flossing once daily helps remove food particles and plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that can cause tooth decay and gum disease.
- Use fluoride toothpaste: Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it more decay-resistant. Choosing toothpaste with fluoride is a simple step to prevent tooth infections.
- Eat a balanced diet and limit sugary snacks: Foods high in sugar and carbohydrates can contribute to tooth decay, leading to infections. Eating a balanced diet and limiting these snacks can protect your teeth.
- Avoid tobacco products: Smoking or using tobacco products can harm your gums, making them more susceptible to infection and slowing down the healing process.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings is crucial. These visits can help identify early signs of problems, like cavities or gum disease before they escalate into serious infections.
- Use mouthwash: Antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in your mouth. Adding this to your oral hygiene routine can further protect against tooth infections.
- Drink plenty of water: Water helps wash away food particles and bacteria from your mouth, reducing the risk of tooth decay.
How do you treat hair loss from alopecia areata?
Treating hair loss from alopecia areata involves stimulating hair growth and managing the autoimmune response. There are several effective treatments available:
1. Bio Pilixin Serum By Scandinavian Biolabs
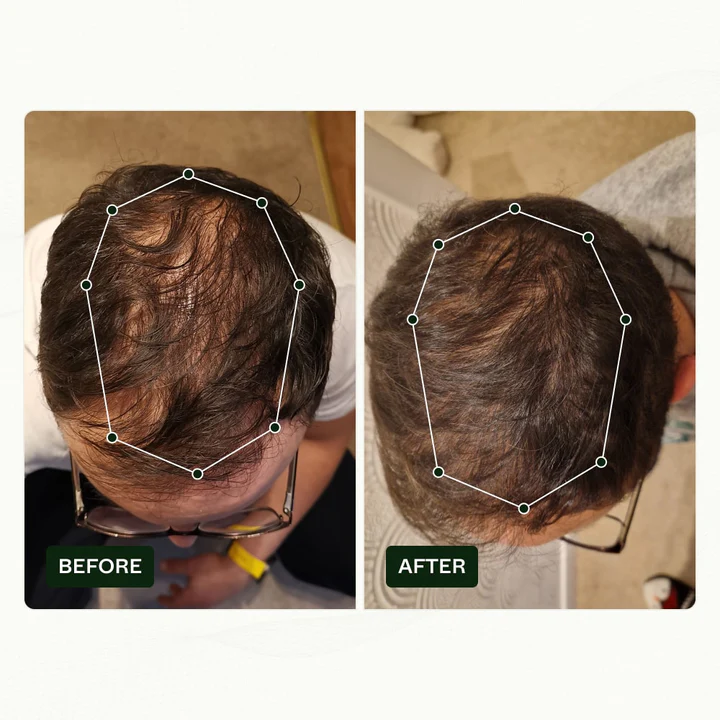
In exploring the surprising links between oral health and hair wellness, the Bio-Pilixin serum emerges as a beacon of hope for those facing hair loss, potentially connected to conditions like alopecia areata.
Leveraging a novel blend of botanical growth factors and peptides, Bio-Pilixin has been clinically proven to combat hair loss in 93% of participants in just 45 days.
Its powerhouse ingredient, Capilia Longa, revitalizes dormant hair follicles, while Niacinamide and Vanillyl Butyl Ether work together to boost scalp microcirculation, ensuring optimal nutrient delivery.
This serum supports hair growth from the root and nurtures the whole hairline and cuticle, creating a nurturing environment for hair restoration.
With a generous 150-day money-back guarantee, trying Bio Pilixin Serum is a risk-free step toward reclaiming your hair's vitality, aligning with our insights on maintaining overall health for hair growth.
2. Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a topical treatment applied directly to the scalp and is known for its efficacy in promoting hair growth and slowing hair loss. It works by enlarging hair follicles and prolonging the growth phase of the hair cycle, making it beneficial for alopecia areata patients.
Although its exact mechanism is not fully understood, its ability to improve blood flow to the scalp may contribute to its effectiveness.
3. Finasteride
Finasteride is an oral medication primarily used to treat male pattern baldness. Still, it can also be effective in alopecia areata by inhibiting the body's production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that can shrink hair follicles.
While it's not universally effective for alopecia areata, it has shown promise in some cases, particularly in combination with other treatments.
4. PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma)
PRP therapy involves drawing a patient's blood, processing it to enrich for platelets, and then injecting it into the scalp. This process stimulates hair follicles by releasing growth factors that promote healing and hair growth.
It's becoming increasingly popular for treating alopecia areata, offering a natural alternative by harnessing the body's healing capabilities.
5. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular activity and promote hair growth. It's a non-invasive treatment that can improve hair density and thickness by enhancing blood circulation to the scalp and reducing inflammation.
LLLT is suitable for mild to moderate alopecia areata and can be used with other treatments.
6. Hair Transplant
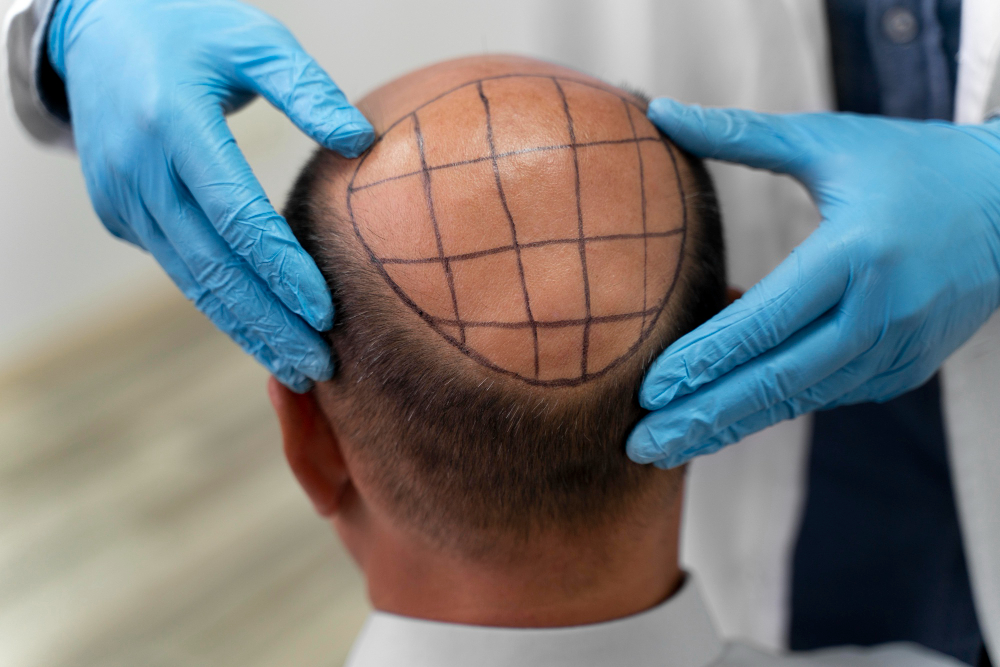
For more advanced cases of alopecia areata where other treatments fail, a hair transplant may be considered. This procedure involves transferring hair follicles from one part of the scalp (usually the back) to the balding or thinning areas.
While effective, it's typically recommended only for patients with stable conditions, as alopecia areata can recur in the transplanted areas.
Conclusion
Treating hair loss, especially from alopecia areata, involves various approaches such as Minoxidil, Finasteride, PRP, Low-Level Laser Therapy, and Hair Transplants. Each method targets hair regrowth differently, offering hope and solutions for those affected.
Additionally, the Bio-Pilixin serum emerges as a promising product, combining botanical growth factors and peptides to significantly reduce hair loss, showcasing impressive clinical results.
This comprehensive approach to hair loss treatment underscores the importance of addressing symptoms and underlying causes, including oral health issues.
FAQs
Can tooth decay directly cause hair loss?
Tooth decay does not directly cause hair loss, but the infections resulting from untreated decay can lead to systemic health issues that may indirectly affect hair growth.
How does oral health impact overall hair health?
Poor oral health can lead to infections and inflammation that might disrupt the body's natural functions, including those responsible for hair growth, potentially exacerbating conditions like alopecia areata.
Is it necessary to treat tooth infections to prevent hair loss?
While treating tooth infections is crucial for overall health, doing so can also mitigate any potential indirect effects on hair loss by reducing systemic inflammation and ensuring the body functions optimally.
References:
-
https://www.nbcnews.com/health/health-news/female-hair-loss-menopause-treatment-study-rcna16389
-
https://www.prevention.com/beauty/a39228765/female-hair-loss-menopause-women-over-50-study/
Read more:
- The Only Mature Hairline Guide You'll Need. 2024 Edition.
- Transitioning To Grey Hair with Highlights: A Simplified Guide






