Experiencing hair loss and thinning hair during menopause is a common concern for many women. Hormonal changes can impact scalp health, leading to challenges like reduced hair density and slower hair growth.
Fortunately, the right shampoo for thinning hair due to menopause can make a real difference. Formulated with essential ingredients like biotin, keratin, and caffeine, these shampoos work to stimulate hair follicles, reduce hair loss, and promote hair growth.
Whether you’re seeking a sulfate-free shampoo or products that moisturize and strengthen hair, these 11 options are designed to address these challenges and deliver real results.
Let’s explore the best shampoos for thinning hair due to menopause!
Table of content
Does menopause cause hair loss?
Yes, menopause can cause hair loss. Menopausal hair loss is most commonly caused by hormonal changes that occur during menopause. As estrogen levels decline, the hair follicle may shrink, causing the hair growth cycle to slow down.
This can lead to the shedding of more hair than normal and thinning hair on the scalp.
Other factors that may contribute to menopausal hair loss include:
- Genetics: Women with a family history of female pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia) are more susceptible.
- Stress: High stress levels can disrupt the hair growth cycle and cause excessive shedding.
- Medical conditions: Thyroid disorders , autoimmune diseases, and other conditions may trigger hair loss.
- Medications: Blood thinners, birth control pills, and other drugs may cause thinning as a side effect.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Low iron, zinc, amino acid, vitamin D, vitamin C, and vitamin A can impair hair regrowth and cause hair breakage.
- Hair styling: Excessive dyeing, bleaching, brushing, and heat styling can cause frizzy hair and damaged hair.
The hormonal change of menopause is usually the main culprit, but hair loss can be multifactorial during this time.
As your leading source for hair health information over the past 4 years, we never compromise on accuracy. When it comes to your health, you deserve information you can truly rely on - and earning your trust is our top priority.
Here's how Scandinavian Biolabs ensures every piece of content meets the highest standards of accuracy and integrity:
- Credentialed Experts: Our reviewers are actively practicing doctors and medical researchers
- Stringent Reviews: Content undergoes rigorous editing by subject specialists and review by a practicing doctor.
- Evidence-Based: We rely on well-established research from trusted scientific sources like peer-reviewed journals and health authorities.
- Full Transparency: Our editorial standards, writer credentials, reviewer credentials, correction process, and funding are all publicly documented.
- Independent Voice: While we do promote products, we operate in a vacuum to business operations. Our main goal is just an unwavering commitment to providing medically-sound guidance.
You can count on Scandinavian Biolabs to consistently deliver the trustworthy health information you deserve. Read our Editorial Standards.
Our ranking system
When reviewing the best shampoo for menopausal hair, we rank them based on 15 important criteria including clinical studies, customer service, low side effects, science-backed formulas, suitability for any hair type, natural ingredients, sustainability, money-back guarantees, value, availability, customer reviews, and being free of harmful chemicals.
Our top pick passed all 15 of these criteria making it thebest shampoo for menopausal dry hair and thinning.
Shampoos for Menopausal Hair Loss
Here are 11 best shampoos for thinning hair due to menopause & itchy scalp.
🔹 Best Overall: Scandinavian Biolabs Hair Strength Shampoo – Scientifically designed to strengthen hair and reduce hair loss.
🔹 Best for Hormonal Hair Loss: Plantur 39 Phyto-Caffeine Shampoo – Formulated to combat hair thinning caused by menopause.
🔹 Best Moisturizing Formula: Pura D'or Anti-Hair Thinning Shampoo and Deep Moisturizing Conditioner – Hydrates while encouraging hair growth.
🔹 Best Stimulating Shampoo: ThickTails Stimulating Hair Shampoo – Boosts hair follicle health and promotes thicker strands.
🔹 Best for Daily Use: Bellisso Biotin Shampoo and Treatment Conditioner – Infused with biotin for stronger, fuller hair.
🔹 Best Anti-Aging Formula: Alterna Haircare Caviar Anti-Aging Clinical Densifying Shampoo – Restores density and fights aging-related hair thinning.
🔹 Best for Thinning Hair: Nioxin System 4 – Targets noticeably thinning hair with a multi-step system for scalp and strand health.
🔹 Best Botanical Formula: Botanical Hair Growth Lab Shampoo – Packed with natural extracts to support hair growth and scalp care.
🔹 Best Budget-Friendly: Renpure Originals Biotin & Collagen Thickening Shampoo – Affordable and effective for adding volume and strength.
🔹 Best for Gray Hair: Jhirmack Silver Brightening Shampoo – Brightens silver and gray hair while maintaining hair health.
🔹 Best Salon-Quality: Kérastase Densifique Bain Densité Shampoo – Luxurious shampoo that increases hair fullness and density.
With these picks, you can safely and confidently say goodbye to dry hair, thinning hair and frizzy hair from menopause.
1. Scandinavian Biolabs Hair Strength Shampoo

Topping our list, the best shampoo for thinning hair due to menopause is none other than the Scandinavian Biolabs Hair Strength Shampoo.
You can witness an astounding clinically tested 93% reduction in hair loss and a remarkable up to 73% improvement in hair density with the Bio-Pilixin Serum. That's 9 out of 10 users.
Powered by nature.
Capilia Longa, derived from turmeric, alongside niacinamide, amino acids, and caffeine, strengthens and revitalizes your hair. These ingredients work together for thicker, shinier locks.
Vegan and safe for daily use.
Made in Denmark to the strict Scandinavian standards, our 100% vegan, cruelty-free formula is also free from sulfates, parabens, and phthalates.
Suitable for your hair types
Whether you have color treated hair, oily hair or curly hair, this shampoo is suitable for all hair types due to our gentle formula
Embrace Your Hair’s Potential
Say goodbye to thinning challenges. Welcome back strength, shine, and volume. Your journey to confident, youthful hair begins here.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Plantur 39 Phyto-Caffeine Shampoo'

Plantur 39's shampoo harnesses science-backed ingredients to support hair already weakening due to hormonal shifts.
While not a miracle solution, it offers a natural way to complement healthy lifestyle habits from within.
Those dealing with hair loss tied to menopause may find it helps improve hair's condition when used alongside a diligent self-care regime.
Overall customer feedback has been largely positive, but tolerance also varies from person to person.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
3. Pura D'or Anti-Hair Thinning Shampoo And Deep Moisturizing Conditioner

PURA D'OR's shampoo and conditioner utilize natural compounds to complement hair's own regenerative processes from within. While not a magic solution, most customer feedback credits the routine with improvements like reduced shedding over time.
Those prioritizing organic ingredients in haircare may find this set helps promote hair health naturally in cases of thinning. However, only consistent use paired with a supportive lifestyle can reliably support genetic or medical causes.
Overall, it offers a generally well-tolerated option worth considering.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
4. ThickTails Stimulating Hair Shampoo

ThickTails Shampoo aims to bolster hair already facing challenges through natural, tailored ingredients making it a great shampoo for perimenopause.
While not a solution for severe loss, most feedback describes improvements to volume and strength over consecutive uses. Its formulation deserves consideration among options for hormonal thinning.
However, only consistent trials paired with an overall healthy lifestyle plan can reliably nurture hair in addressing complex, multi-factorial causes of loss.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
5. Bellisso Biotin Shampoo And Treatment Conditioner

This shampoo/conditioner did not achieve noticeable impacts for all users as formula tolerance can vary greatly.
However, gentle formulations with biotin and input from industry practitioners remain an option worth considering for some seeking dedicated thickening support.
Consistent use paired with a supportive routine offers the best chance of experiencing claimed outcomes.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
6. Alterna Haircare's Caviar Anti-Aging Clinical Densifying Shampoo

Alterna Haircare's Caviar Anti-Aging Clinical Densifying Shampoo is crafted to address the challenges of fine hair, particularly for those experiencing age-related changes. This formula aims to provide a luxurious, nurturing experience while focusing on improving hair strength and density.
While it's not a complete solution for hair loss, it's designed to be part of a comprehensive approach to healthy hair growth, especially for aging hair.
The majority of users report satisfaction with the product, noting visible improvements, although individual experiences may vary.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
7. Nioxin System 4

Nioxin System 4 is a specialized shampoo solution designed for noticeably thinning, fine, and chemically treated hair. It aims to rejuvenate hair by cleansing the scalp and providing thicker, fuller-looking hair.
It's part of a holistic approach to hair care, especially beneficial for those dealing with thinning related to various factors, including chemical treatments.
Reactions are predominantly positive with a few negative ones, with many customers appreciating the changes in their hair's appearance and feel.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
8. Botanical Hair Growth Lab Shampoo

Botanical Hair Growth Lab offers an excellent shampoo for thick, strong, and healthy hair. This anti-hair loss organic formula is not only suitable for women experiencing hair fall due to menopause but also addresses androgenetic alopecia and postpartum hair loss.
It comprises more than 15 natural ingredients, including aloe vera leaf juice, apple stem cell extract, chamomile flower extract, green tea extract, argan oil, and rosemary oil.
Enriched with essential vitamins, this natural scalp-stimulating formula is free of SLS and parabens. Botanical Hair Growth Lab is the right choice for you if you are looking for a pure and natural product to fight hair loss.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
9. Renpure Originals Biotin & Collagen Thickening Shampoo

Renpure Originals Biotin & Collagen Thickening Shampoo is a popular choice among women for volumizing and thickening menopausal hair.
This plant-based shampoo features biotin and collagen as primary ingredients that work together to thicken, volumize, nourish, and moisturize the scalp and hair.
Free from sulfates and parabens, this shampoo is gentle and safe for all hair types. By using Renpure's Thickening Shampoo, you can keep your hair healthy, thick, and shiny.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
10. Jhirmack Silver Brightening Shampoo

This silver brightening shampoo is an excellent option if you are looking for a shampoo specifically designed for grey hair.
Formulated with green tea extract, folic acid, and CoQ10, this set also helps to strengthen hair, fight against heat damage and environmental pollutants, and reduce dry menopausal hair.
The macadamia nut oil in the set moisturizes the hair and scalp without leaving a greasy residue.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
11. Kérastase Densifique Bain Densité Shampoo

Kérastase Densifique Bain Densité Shampoo is a good solution for those who want thicker, healthier-looking hair. It's infused with ceramides to protect your hair from damage and hyaluronic acid to increase hydration, leaving your hair silky and voluminous.
This shampoo's unique formula helps improve hair density, providing a more nourished scalp and lustrous hair. Regularly using this shampoo also helps reduce hair breakage and split ends.
It is a decent solution for menopausal hair thinning.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
What's the best hair growth shampoo for menopause?
Our pick for the best shampoo for thinning hair due to menopause is the Scandinavian Biolabs Hair Strength Shampoo.
Here's why it's the perfect pick for menopausal thinning hair and itchy scalp:
- Combats Menopause Hair Loss: This shampoo for menopause gently cleanses your scalp, removing excess oil that can clog hair follicles and hinder growth.
- Natural Boost: Packed with nature-inspired ingredients, it nourishes your scalp to create a healthy environment for hair to thrive.
- Say Goodbye to Greasiness: No more limp, lifeless locks! This sulfate-free formula cleanses without stripping away natural oils, leaving your hair feeling fresh and vibrant.
- Daily Support: Gentle enough for everyday use, you can experience the fortifying benefits day after day.
- Luxurious Eucalyptus Aroma: Enjoy a spa-like experience every time you shower with the invigorating scent of eucalyptus.
It just happens to also top our test for the best shampoo for perimenopause hair loss.
How do shampoos for menopausal hair fall work?
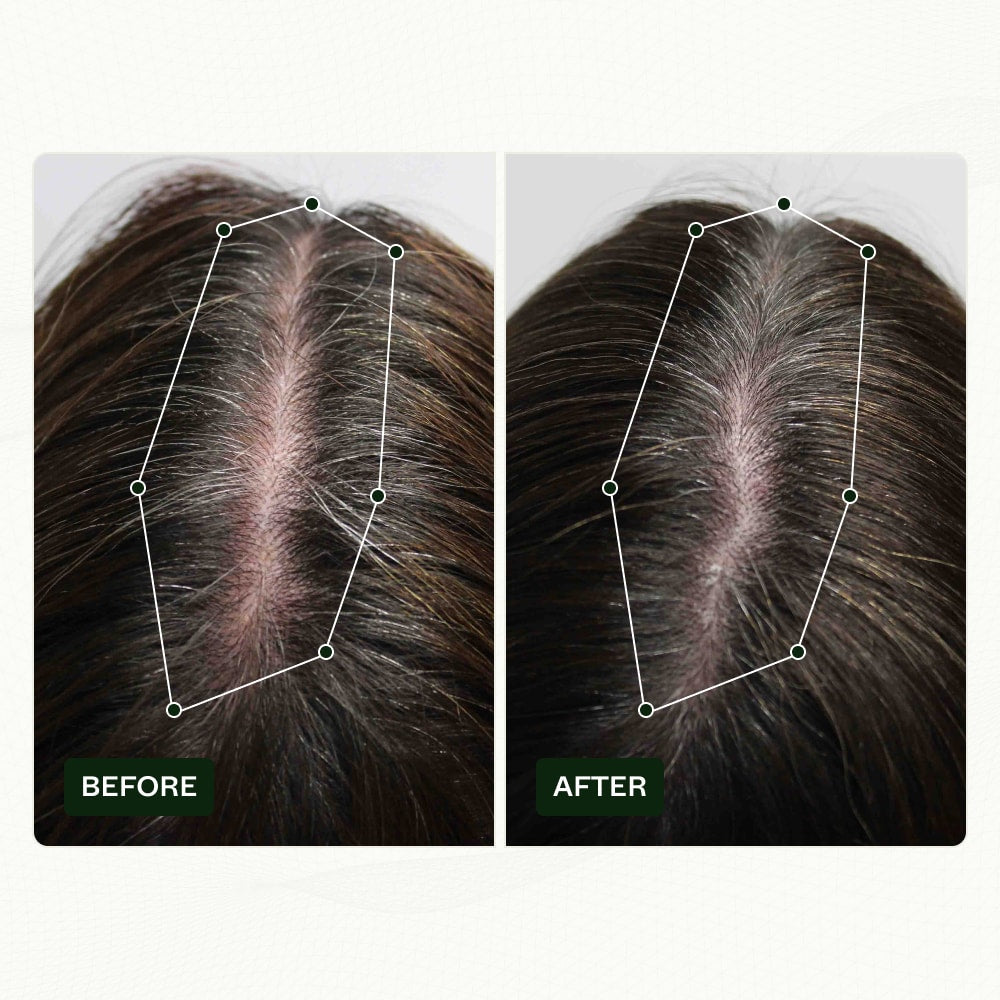
The best shampoo for thinning hair over 60 typically contain biotin, keratin, caffeine, and essential oils to promote growth by improving scalp health and strengthening the hair follicle.
While biotin and caffeine have shown some promise in small studies , evidence of their efficacy is still limited.
Minoxidil and ketoconazole are common additions, which may help prevent hair loss through different mechanisms.
Though potentially effective, more research is needed on these shampoos to fully understand their benefits for treating hair loss.
What to look for in the best shampoo for thinning hair due to menopause?
When looking for the best shampoo for menopausal hair, consider an ingredient that helps balance hormones, stimulates hair growth, and strengthens the hair strands.
Some key ingredients include:
- Phytoestrogens: These plant-based compounds mimic estrogen and can help balance hormones.
- Biotin : A vitamin B that supports hair growth and strength.
- Caffeine: Stimulates hair strands and promotes growth.
- Keratin: A protein that strengthens hair strands and prevents breakage.
- Shea butter: Moisturizes the scalp and hair strands.
- Coconut oil: Moisturizes and reduces protein loss from hair.
- Castor oil: Promotes hair regrowth and increases blood circulation to the scalp.
- Saw palmetto: Contains fatty acids and sterols that can block DHT formation to prevent thinning hair.
Finally, choose a menopause shampoo free from harsh chemicals, such as sulfates and parabens, which can further damage hair and irritate scalp.
Read this: How to regrow hair?
What makes a shampoo effective for menopausal hair?
When dealing with thinning hair and hair loss due to menopause, it’s important to choose a shampoo that addresses both the symptoms and underlying causes. An effective shampoo should promote hair growth, enhance scalp health, and restore hair density. Look for shampoos with essential ingredients like biotin, keratin, and caffeine, which can help stimulate hair follicles and strengthen each strand. Formulas that balance the scalp’s pH, remove excess oils, and support hydration are key to maintaining healthy hair during menopause.
The role of ph balancing in scalp health
Maintaining the right pH balance is crucial for scalp health, particularly during menopause when hormonal changes can lead to scalp dryness or oiliness. A pH-balanced shampoo helps maintain the scalp’s natural barrier, preventing irritation and dryness, while also ensuring that hair follicles are nourished. Using a shampoo with the proper pH can improve scalp health, which in turn supports healthy hair growth and reduces issues like flaky scalp and buildup.
Importance of sulfate-free formulas
As you seek effective solutions for thinning hair due to menopause, opting for sulfate-free shampoos is essential. Sulfates can strip the hair of natural oils, leaving it dry and more prone to breakage. Sulfate-free formulas provide a gentler cleanse, preserving moisture in the hair and scalp. These shampoos are especially beneficial for those with sensitive scalps or dry hair, making them an excellent choice for menopausal women looking to combat hair loss and scalp irritation.
Deep cleansing for scalp revitalization
A deep cleansing shampoo is key for revitalizing the scalp, especially when dealing with menopausal hair changes. It helps to remove product buildup, excess oils, and impurities that may clog hair follicles, preventing healthy hair growth. Look for products that not only cleanse the scalp but also promote blood circulation to the hair follicles, helping to stimulate hair growth and support overall scalp health. A refreshed scalp environment can lead to stronger, more resilient hair as it regrows.
How to use hair loss shampoos for menopause
When dealing with hair loss and thinning hair due to menopause, choosing and using the right shampoo can make a significant difference. Follow these steps to ensure you're maximizing the benefits of your shampoo for thinning hair due to menopause and achieving the best results.
Step 1: choosing the right shampoo
The first step in addressing hair loss is selecting the right shampoo. Look for sulfate-free formulas that are gentle on the scalp and hair. Opt for shampoos containing biotin, keratin, and caffeine, which are known to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. Ensure the shampoo is specifically designed for menopausal hair to address concerns like dry scalp, thinning hair, and loss of density. A pH-balanced shampoo will help maintain the health of your scalp and keep your hair in optimal condition.
Step 2: application techniques
Proper application is key to getting the most from your shampoo. Start by wetting your hair thoroughly with warm water. Apply a generous amount of shampoo to your scalp and gently massage it in using your fingertips—avoid using your nails, as this can cause irritation. Focus on the roots, where most hair loss occurs, and allow the shampoo to sit for a few minutes to let the active ingredients penetrate the scalp. Rinse thoroughly with cool water to close the hair cuticles and retain moisture.
Step 3: frequency of use
For best results, use your hair loss shampoo consistently, typically 2-3 times a week. If you have a more oily scalp, you may want to increase the frequency to daily use, but always listen to your scalp. If you have a dry or sensitive scalp, using the shampoo too often can cause irritation. Balance is key—regular use without over-washing is important for maintaining healthy hair growth and scalp health.
Step 4: complementary products
To enhance the effects of your shampoo, consider using complementary products like conditioners, serums, and scalp treatments. A moisturizing conditioner can help hydrate and nourish your hair, preventing dryness. Look for serums or leave-in treatments that contain biotin or caffeine to further stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. Scalp massage oils or vitamin-rich treatments can improve circulation and provide additional nourishment to your hair roots.
Step 5: monitoring progress
After starting your hair loss shampoo routine, be patient and monitor your progress over time. While results can vary, you should start to see improvements in hair density and reduced hair loss within 4-6 weeks of consistent use. Keep track of changes in your hair’s health, such as growth, strength, and thickness. If you notice any adverse effects, such as increased dryness or irritation, adjust the frequency of use or switch to a different shampoo formula. Regular monitoring will help you determine whether the product is working effectively for your hair type and menopausal needs.
How to regrow hair from menopausal thinning hair?
While shampoos can help, more substantial thinning hair may require clinical-strength solutions. Here are some best products for menopausal hair loss, recommended by experts:
Bio-Pilixin
Our Bio-Pilixin® Serum has been specifically formulated to help reduce hair thinning associated with menopause.
As estrogen levels decline during perimenopause and menopause, it can lead to excess hair shedding and thinning.
This targeted serum contains a proprietary blend of plant growth factors and stem cell technology to nourish hair follicles impacted by hormonal changes.
Minoxidil
As the only FDA-approved topical for female hair loss, it stimulates regrowth by improving blood flow to follicles. Look for a 2 or 5% topical solution.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
This non-invasive treatment uses light therapy to boost cell metabolism and stimulate regrowth factors from the scalp. Multiple sessions are usually required but side effects are minimal.
Hair supplements
Supplements like marine collagen peptides, isoflavenes, and zinc target hair loss at the source with anodyne support. This can certainly build the foundation for thicker hair.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
Using your own platelet-rich plasma, this technique harnesses healing properties to rejuvenate follicles from within. Typically a series of 3-6 monthly injections is needed.
Hair transplant
For thinning areas, follicular unit transplant (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE) can restore a natural appearance by surgically placing hair grafts.
At home keratin treatment
Smooth keratin bonds temporarily repair hair shafts and add shine/volume to give the impression of fuller hair.
Diagnosing female hair loss can be complex, so an expert evaluation is important to determine the best customized, clinical-strength regimen for your thin hair concerns and regrowth goals after menopause.
Popular myths about menopausal hair loss and shampoos
There are many myths surrounding menopausal hair loss and the shampoos marketed to address it. While some shampoos can be effective in promoting hair growth and improving scalp health, it’s important to separate fact from fiction. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths about hair loss during menopause and the shampoos designed to treat it.
Myth: shampoo alone can reverse hair loss
One common misconception is that using a shampoo for thinning hair will automatically reverse hair loss. While a good shampoo can help improve scalp health, reduce hair loss, and promote hair growth, it cannot fully restore hair growth on its own. Menopausal hair loss is often caused by hormonal imbalances, and shampoo is just one part of the solution. For the best results, shampoos should be paired with other treatments, such as serums, scalp massages, and lifestyle changes, to address the root causes of hair thinning.
Myth: all shampoos are created equal
Not all shampoos for thinning hair are the same. Shampoos vary in their ingredients, formulation, and effectiveness, and what works for one person may not work for another. Shampoos that contain biotin, keratin, caffeine, or sulfate-free formulas are often better suited for menopausal women experiencing hair loss and scalp health issues. It’s essential to choose a shampoo designed specifically for menopausal hair, as it will address the unique needs and challenges that arise during this stage, such as hormonal changes and scalp dryness.
Myth: hair loss is inevitable during menopause
Many women believe that hair loss is inevitable during menopause. While it’s true that hormonal changes can lead to thinning and loss of hair, it is not a given for every woman. The degree of hair loss varies from person to person, and some women experience little to no thinning at all. With the right products, such as shampoos for thinning hair, along with lifestyle adjustments, it's possible to maintain healthy hair and slow down the effects of menopausal hair loss.
Myth: natural ingredients are always better
While natural ingredients are often marketed as being the best option for hair care, they are not always the most effective when it comes to treating menopausal hair loss. Some natural ingredients, such as essential oils or herbal extracts, may have beneficial properties, but they may not always be as powerful as scientifically-backed ingredients like biotin, caffeine, or keratin. It’s important to strike a balance between natural and active ingredients to get the most effective results for hair growth and scalp health during menopause. Always choose shampoos with a well-researched blend of ingredients.
Conclusion
Finding the right shampoo for thinning hair during menopause is essential for maintaining hair health and promoting stronger, fuller strands. The best shampoos are designed to nourish the scalp, stimulate hair growth, and strengthen fragile hair while addressing hormonal changes that contribute to hair loss.
When choosing a shampoo, look for key ingredients like biotin, keratin, caffeine, and botanical extracts that support hair density and scalp health. Additionally, opt for sulfate-free formulas to prevent further dryness and damage.
With consistent use and the right product for your hair type, you can improve hair texture, reduce breakage, and restore confidence in your hair’s appearance. Whether you're looking to stimulate new growth or maintain existing strands, these carefully curated shampoos provide effective solutions for managing menopause-related hair thinning.
References






