Rogaine may be a popular hair loss treatment, but it’s not the only solution.
In 2025, a variety of effective alternatives—both natural and drug-based—offer promising results for promoting hair growth and reducing hair thinning.
This guide highlights the 11 best options, ranging from plant-based treatments to clinically-proven formulas, providing diverse choices to suit different hair care needs. Whether seeking a gentler approach or a powerful medical solution, these alternatives deliver real, visible improvements for healthier, fuller hair.
Table of content
What is Rogaine?
Rogaine addresses hair loss and promotes hair regrowth by enhancing blood flow to hair follicles, thanks to its ability to widen blood vessels in the scalp.
This increased blood flow helps to revive shrunken hair follicles, enlarging them and extending their growth phase, ultimately leading to thicker, longer hair and slowing the process of hair thinning and loss.
As your leading source for hair health information over the past 4 years, we never compromise on accuracy. When it comes to your health, you deserve information you can truly rely on - and earning your trust is our top priority.
Here's how Scandinavian Biolabs ensures every piece of content meets the highest standards of accuracy and integrity:
- Credentialed Experts: Our reviewers are actively practicing doctors and medical researchers
- Stringent Reviews: Content undergoes rigorous editing by subject specialists and review by a practicing doctor.
- Evidence-Based: We rely on well-established research from trusted scientific sources like peer-reviewed journals and health authorities.
- Full Transparency: Our editorial standards, writer credentials, reviewer credentials, correction process, and funding are all publicly documented.
- Independent Voice: While we do promote products, we operate in a vacuum to business operations. Our main goal is just an unwavering commitment to providing medically-sound guidance.
You can count on Scandinavian Biolabs to consistently deliver the trustworthy health information you deserve. Read our Editorial Standards.
How does Rogaine work for hair loss?
Rogaine (minoxidil) works by targeting androgenetic alopecia (hereditary hair loss) through multiple mechanisms, though its exact pathways remain partially understood. Here’s a breakdown of its key effects:
Mechanisms of Action
Follicle Reactivation:
- Reverses follicle miniaturization: Minoxidil enlarges shrunken hair follicles, which are a hallmark of hereditary hair loss.
- Extends the anagen phase: It prolongs the active growth phase of hair follicles, allowing thicker, longer hair to develop.
Blood Flow Enhancement: Acts as a vasodilator, increasing blood flow to the scalp and delivering more oxygen/nutrients to follicles.
Hair Growth Stimulation: Tricho-Prime® Technology: Rogaine’s formula primes the scalp for regrowth by enhancing protein production and follicle activity.
Effectiveness and Considerations
FDA Approval: Clinically proven for male/female pattern baldness, particularly at the scalp’s vertex (crown area).
Results Timeline:
- Initial shedding: Temporary hair loss may occur within 2 weeks as follicles transition to the growth phase.
- Visible regrowth: Noticeable improvement typically begins after 4 months, with peak results around 8–12 months.
Continuous Use Required: Effects are reversible; discontinuation leads to hair loss returning to baseline levels.
What are the side effects of Rogaine?
Rogaine is generally well-tolerated, but like any medication, it can have side effects, particularly when used topically on the scalp. These include:
- Itching, redness, or irritation at the site where Rogaine is applied, potentially affecting the scalp's environment for hair follicles.
- Unwanted facial or body hair growth
- Dizziness or faintness
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Weight gain, swelling of the hands or feet (edema)
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain
11 Best Alternatives to Rogaine
Here are some of the best alternatives to Rogaine for promoting hair growth and reducing hair loss:
🔹 Bio-Pilixin Serum – A plant-powered serum clinically developed to stimulate hair growth and strengthen follicles.
🔹 Essential Oils – Natural oils like rosemary, peppermint, and lavender can improve scalp health and encourage hair regrowth.
🔹 Scalp Massage – Increases blood circulation to the scalp, which may help stimulate hair follicles and support hair growth.
🔹 Saw Palmetto – A natural DHT blocker that may slow hair loss and promote hair regrowth by preventing hormone-related thinning.
🔹 Spironolactone – A prescription medication that reduces androgen levels, which may help treat hormonal hair loss, especially in women.
🔹 Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) – Non-invasive laser treatments that stimulate hair follicles and promote thicker, healthier hair growth.
🔹 Finasteride (Propecia) – An oral medication for men that blocks DHT, the hormone responsible for male pattern baldness.
🔹 Hair Transplant Surgery – A permanent solution where healthy hair follicles are transplanted to areas experiencing thinning or baldness.
🔹 Capsaicin – Found in chili peppers, this compound may promote hair growth by improving blood flow to the scalp.
🔹 Caffeine – Applied topically, caffeine can stimulate hair follicles and potentially extend the hair growth cycle.
🔹 Redensyl – A plant-based compound that targets hair follicle stem cells to promote growth and reduce shedding.
1. Bio- Pilixin Serum
Bio-Pilixin Serum offers an advanced, plant-based alternative to Rogaine and minoxidil, designed to combat hair thinning and support hair regrowth.
Utilizing stem cell technology, the serum directly nurtures hair follicles. Clinical tests showed significant reductions in hair loss and improved hair density within 45 days.
The formula is 100% vegan, rigorously reviewed for efficacy, and includes powerful ingredients like Capilia Longa, which has been shown to reduce hair loss by up to 89% and improve hair density by 52%.
Additionally, Niacinamide and Vanillyl Butyl Ether are included to strengthen hair and enhance scalp circulation, making Bio-Pilixin a potent, nature-inspired solution for hair loss.
2. Essential oils
Essential oils like rosemary, peppermint, and pumpkin seed offer a natural alternative to Rogaine for hair growth. When diluted with carrier oils like castor or coconut oil, these plant-derived oils help combat hair loss.
Applying the mixture to clean hair once or twice a week can enhance absorption and effectiveness, providing a simple, low-maintenance hair care routine.
3. Scalp massage
Scalp massage stimulates hair growth by enhancing blood circulation, similar to how Minoxidil works. This technique promotes hair follicle health and is best incorporated during shampooing or with specialized tools.
While effective in preserving existing hair, it may not regrow lost hair and should be done gently to avoid exacerbating hair loss during shedding phases.
4. Saw palmetto
Saw palmetto extract, derived from the saw palmetto tree, may help prevent hair loss by inhibiting the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT, a key factor in hair thinning.
While popular among those seeking natural alternatives, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy compared to traditional hair growth medications.
5. Spironolactone
Spironolactone, used primarily for high blood pressure and hormonal acne, also treats hair loss by targeting androgen-related causes.
It is particularly effective for women but may have side effects in men, such as breast tissue growth and erectile dysfunction, highlighting the need for personalized hair loss treatments.
6. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
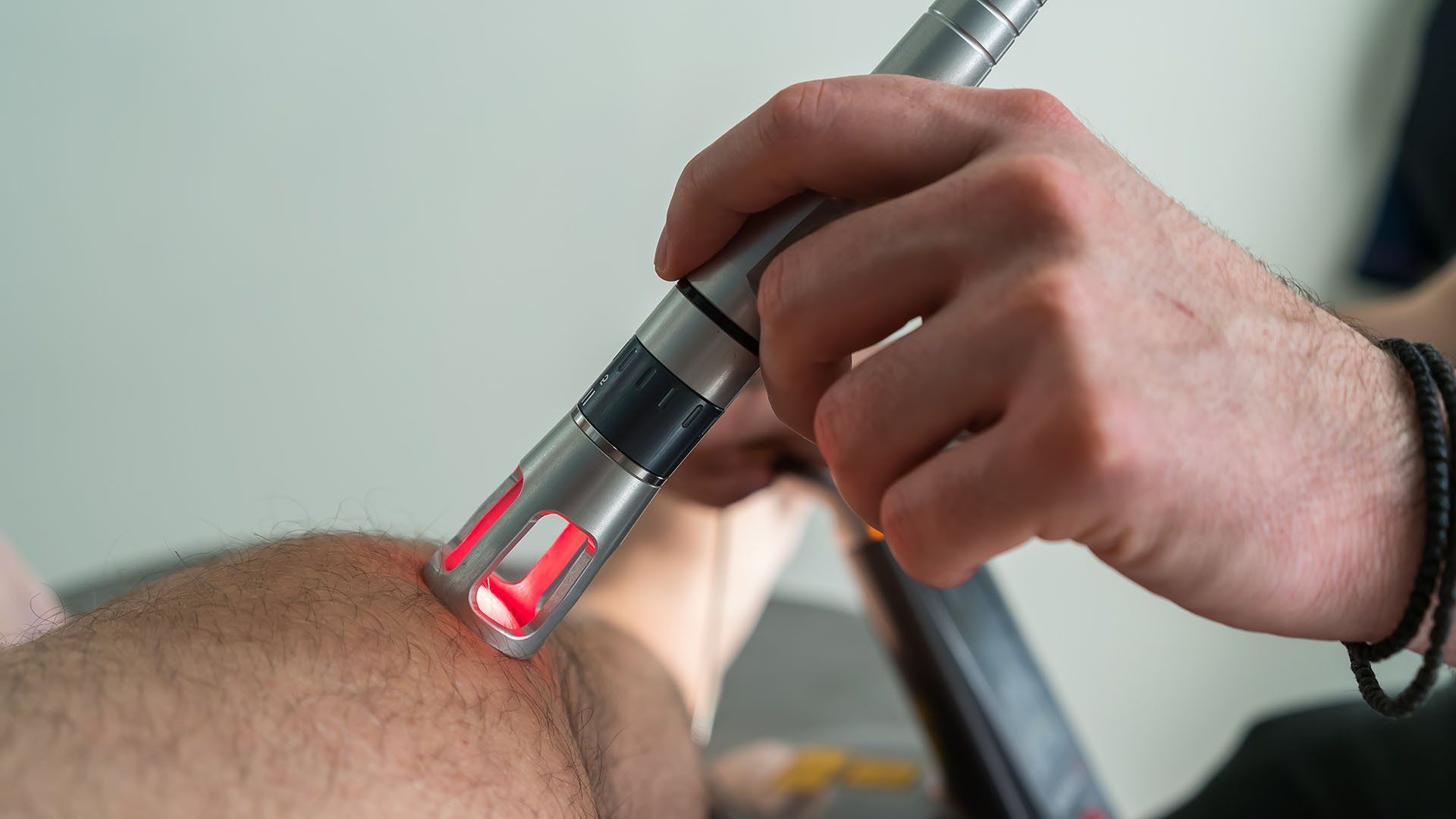

LLLT uses low-intensity light to stimulate cellular activity in the scalp, promoting hair regrowth. This non-invasive, cost-effective therapy not only aids in hair loss prevention but also offers additional health benefits like skin rejuvenation and mood enhancement.
7. Finasteride (Propecia)
Finasteride, an oral medication, combats male pattern hair loss by blocking DHT production, a hormone linked to hair thinning.
It’s highly effective, with many men experiencing hair regrowth and reduced hair loss, supported by extensive research and clinical trials.
8. Hair transplant surgery
Hair transplant surgery offers a long-term solution for hair loss by relocating hair follicles from thicker areas to thinning or bald spots.
Techniques like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) have improved these procedures' natural appearance and success rates, making them a viable option for those seeking a permanent fix.
9. Capsaicin
Capsaicin, a compound found in peppers, has shown the potential to promote hair growth. One clinical trial suggested that oral capsaicin improved hair growth compared to a placebo, though the study was small and combined with isoflavone, making it hard to isolate capsaicin's effects.
Topically, capsaicin can stimulate the growth of vellus hair, but this "peach fuzz" isn't typically the thick hair desired for those combating hair loss.
10. Caffeine
Caffeine is featured in some hair growth shampoos and has been shown in small studies to reduce hair loss progression.
Topical caffeine, often combined with other treatments like minoxidil, can enhance hair thickness and slow down hair loss, offering a more effective solution than minoxidil alone in some cases.
11. Redensyl
Redensyl is a newer hair loss treatment with promising early results. Although more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness, Redensyl shows potential as an alternative to Minoxidil, particularly for those looking for innovative solutions to hair thinning and loss.
Conclusion
In 2025, there are numerous alternatives to Rogaine that cater to various preferences, from natural remedies like essential oils and Bio-Pilixin Serum to advanced treatments like Finasteride and hair transplant surgery.
Each option offers unique benefits, whether you're looking for gentle, plant-based solutions or more intensive medical interventions.
By exploring these alternatives, you can find the right approach to combat hair loss and promote healthy hair growth that suits your needs and lifestyle.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6691938/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5804833/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3500065/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7736953/