Finding the best DHT blocker for women can be a game-changer in managing hair loss and promoting hair growth.
DHT blockers work by inhibiting the hormone dihydrotestosterone, which is known to shrink hair follicles and halt hair production in those suffering from androgenetic alopecia.
In this article, we'll explore the most effective DHT blockers for women, their benefits, and potential side effects, helping you make an informed decision about your hair care routine.
Table of content
9 best DHT blocker for women
These are the 9 best DHT blockers for women:
- Finasteride
- Spironolactone
- Pumpkin Seed Oil
- Saw Palmetto
- Green Tea Extract
- Pygeum Africanum
- Stinging Nettle
- Soy Products
- Zinc Supplements
Finasteride
Finasteride is a prescription-only medication that works by blocking the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to DHT. It can help block DHT from shrinking the hair follicles, thus helping to reduce female hair loss. Finasteride for women is available, though the drug is primarily targeted towards men.
However, it is important to note that women who are pregnant or who may become pregnant should not take this medication, as it may cause damage to a male fetus' developing genitals. It is also associated with some finasteride side effects, such as decreased sex drive, gynecomastia, and increased body hair growth.

Spironolactone
This medication is primarily a diuretic but has anti-androgen effects. It's often prescribed to women experiencing hair loss due to its ability to inhibit the production and action of androgens, like DHT. Spironolactone can be effective in treating female pattern hair loss and hirsutism (excessive hair growth). It's usually well-tolerated but can have side effects like electrolyte imbalances and should not be used during pregnancy.
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Available as a supplement, pumpkin seed oil may help in reducing DHT levels due to its phytosterol content. Studies suggest it can be beneficial for hair growth, especially in women with hair thinning. It's considered a natural DHT blocker and is generally safe with minimal side effects.
Saw Palmetto
This herbal supplement is derived from the fruit of the saw palmetto tree. It's believed to slow down hair loss by reducing the conversion of testosterone to DHT. While more commonly recommended for men, it can also be beneficial for women suffering from hair thinning due to hormonal imbalances. However, its effectiveness in women is less studied than in men.
Green Tea Extract
Rich in antioxidants, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), green tea extract can help in reducing DHT levels. It's thought to promote hair growth and is a popular ingredient in many hair care products. Green tea extract is generally safe, but high doses can have side effects like liver toxicity.
Pygeum Africanum
Derived from the bark of an African cherry tree, this herbal remedy is believed to inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, thus reducing DHT levels. While there's limited research on its efficacy for hair loss in women, it's often used in supplements aimed at hair growth.
Stinging Nettle
Often taken in supplement form, stinging nettle is thought to help block the conversion of testosterone to DHT. It's used for various health conditions, including hair loss. While generally safe, it can interact with certain medications and conditions, so consultation with a healthcare provider is advised.
Soy Products
Soy contains isoflavones, which are thought to have a weak estrogenic effect and may help in reducing DHT. Adding soy products to the diet may have a beneficial effect on hair health in women, particularly those experiencing hormonal imbalances.
Zinc Supplements
Zinc plays a role in hormone regulation and can help in reducing DHT levels. It's often recommended for hair loss and is found in many over-the-counter hair care supplements. While beneficial, excessive intake of zinc can lead to adverse effects and should be taken as per recommended dietary allowances.
As your leading source for hair health information over the past 4 years, we never compromise on accuracy. When it comes to your health, you deserve information you can truly rely on - and earning your trust is our top priority.
Here's how Scandinavian Biolabs ensures every piece of content meets the highest standards of accuracy and integrity:
- Credentialed Experts: Our reviewers are actively practicing doctors and medical researchers
- Stringent Reviews: Content undergoes rigorous editing by subject specialists and review by a practicing doctor.
- Evidence-Based: We rely on well-established research from trusted scientific sources like peer-reviewed journals and health authorities.
- Full Transparency: Our editorial standards, writer credentials, reviewer credentials, correction process, and funding are all publicly documented.
- Independent Voice: While we do promote products, we operate in a vacuum to business operations. Our main goal is just an unwavering commitment to providing medically-sound guidance.
You can count on Scandinavian Biolabs to consistently deliver the trustworthy health information you deserve. Read our Editorial Standards.
What are DHT blockers?
DHT blockers are drugs that inhibit the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that can shrink hair follicles and stop hair growth in those suffering from androgenetic alopecia. By blocking DHT, these medications help preserve hair follicles and maintain hair growth.
The most common DHT blockers are Finasteride and Dutasteride, which inhibit the 5 alpha reductase enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to DHT. While these drugs are often used for male pattern baldness, they are not typically recommended for women.
Spironolactone is another anti-androgen commonly prescribed to women, especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
It's crucial to understand the potential risks associated with DHT blockers, particularly for women, before considering them as a treatment for hair loss.
Are DHT blockers effective for treating hair loss in women?
DHT blockers can improve symptoms of certain types of women’s hair loss, such as female pattern hair loss and frontal fibrosing alopecia. According to Shlomo Widder, MD, "DHT, or dihydrotestosterone, is an androgen hormone that can trigger hair loss in women as estrogen levels decline."
While there is evidence that Finasteride and Dutasteride can be effective for treating female hair loss, these medications are generally not suitable for women, particularly premenopausal women, due to potential risks.
Oral Dutasteride and Finasteride can alter levels of other hormones and interfere with the menstrual cycle and fetal development. Therefore, they are not usually recommended for women, especially those who are pregnant or trying to conceive.
However, topical DHT blockers, like those found in certain shampoos, may provide hair growth benefits without the systemic risks associated with oral medications.
"In my practice, I've seen noticeable results in 3-6 months of use," notes Dr. Widder. "One perimenopausal patient saw her hair loss slow and hair regrow after using a DHT blocker with saw palmetto and stinging nettle. After 6 months her hair was thicker and hair loss stabilized. Studies show these ingredients can reduce DHT up to 32% and 23% respectively."
Are there any side effects of DHT blockers for women?
Yes, DHT blockers can have several side effects for women, with the most serious being potential risks to fetal development. Here are some other possible side effects:
- Changes to the menstrual cycle: This can occur with Spironolactone, Finasteride, and Dutasteride.
- Breast tenderness: Commonly associated with Spironolactone.
- Increased urination: Also a side effect of Spironolactone.
- Skin irritation: Possible with topical DHT blockers.
A guaranteed method to combat female hair loss

This treatment is designed to nourish the scalp. The main active ingredient, Capilia Longa, is intended to support dermal papilla cells, contributing to a balanced hair growth cycle.
With this hair care routine, it aims to support the growth phase of the hair development cycle and manage the rest phase.
For those who are looking to avoid DHT blockers side effects, these products are designed to support the development phase of hair and manage the resting phase of the hair growth cycle.
Hair growth cycle disruptions
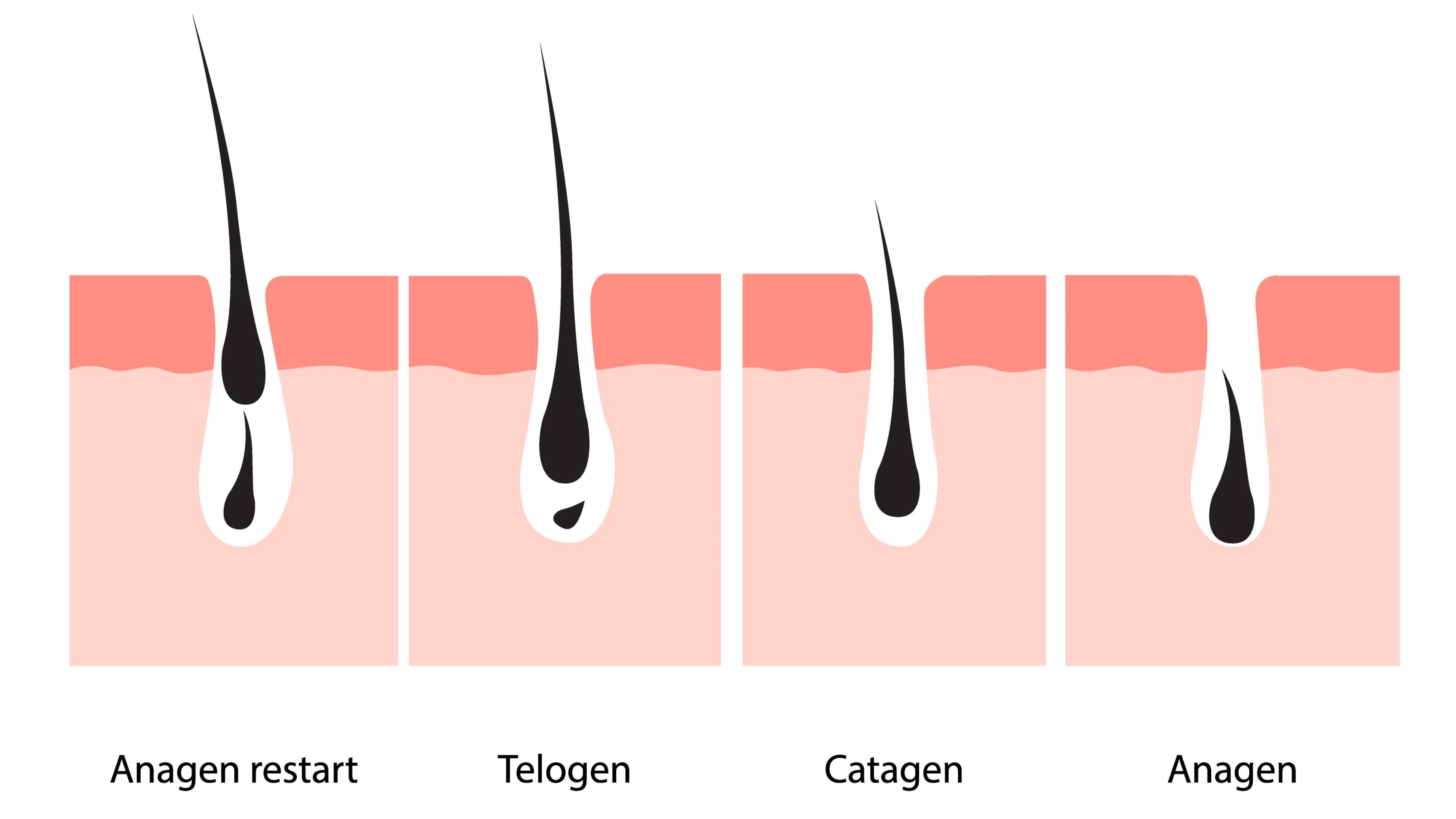
Hairs go through a cycle of growth, shedding, and rest. In a healthy hair cycle, the resting phase is short and followed by the growth phase, when new hair grows. However, many things can disrupt the normal growth process of hair, causing abnormal shedding or even hair loss.
Hormonal imbalance is a common cause of hair loss in women and can be caused by things like pregnancy, menopause, or the use of certain medications. If you don't want to lose more hair, it's important to know the signs of a messed-up hair cycle and do what you need to do to get things back in order.
Women's hormonal imbalance
Hormonal imbalance in women is caused by glands in the endocrine system that don't make hormones as well as they should. This can be due to a variety of diseases and health conditions, such as thyroid or ovarian disorders.
When the hormones are unevenly distributed in the body, it can lead to hair loss, thinning hair, or other types of hair-related issues. To maintain a healthy hormone balance, women should seek professional medical advice and treatment to ensure their bodies are working in harmony.
In the body, hormones are produced by a variety of glands, including:
- Thyroid and parathyroid gland
- The ovaries
- The testes
- Adrenal glands
- Pituitary gland
- Hypothalamus gland
Common health conditions that can cause hormonal hair loss in women

Here are some of the most common health conditions that can lead to hormonal hair loss in women:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – PCOS is a condition that causes the ovaries to produce an excessive amount of androgens, which can result in PCOS hair loss.
- Hypothyroidism – Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid does not produce enough hormones, leading to hair loss.
- Adrenal Insufficiency – Adrenal insufficiency occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones, resulting in hair loss.
- Hyperthyroidism – Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid produces too much hormones, leading to hair loss.
- Menopause – During menopause, a woman’s body stops producing estrogen and progesterone, resulting in menopausal hair loss.
- Postpartum hormonal imbalances – After childbirth, a woman’s hormones can become imbalanced, leading to hair loss.
- Birth control pill - A hormonal birth control pill can cause hormonal imbalance in your body which leads to hair loss.
Read this: Is Your Birth Control Causing Hair Loss?
The role of testosterone in female hair loss
Testosterone is an androgen that both genders produce, but women typically have larger concentrations of estrogen compared to testosterone. When higher than normal levels of testosterone occur, female pattern hair loss may result.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a by-product of testosterone, is a major contributor to hair loss in both men and women. DHT can shrink the size of the hair follicles, resulting in thinning of the hair. Understanding the role of testosterone in female hair loss is important for finding treatments that may be effective.
The relationship between androgenetic alopecia and DHT

The relationship between androgenetic alopecia and DHT is a strong one. In women, elevated levels of testosterone can trigger the production of DHT which can then lead to the development of androgenetic alopecia.
This type of hair loss is caused by androgens like DHT and affects 50 million men and 30 million women in the U.S. to some degree. It is usually characterized by overall thinning of the hair, as opposed to receding hairlines in men.
The amount of testosterone in the body doesn't directly affect hair growth, but the sensitivity to DHT is determined by genetics. For some people, exposure to DHT for long periods can cause persistent damage to the hair follicles, leading to miniaturization.
Fortunately, with proper prevention, hair follicles can be spared from this damage with the use of DHT-blocking interventions.
Conclusion
Hormonal hair loss in women is a prevalent concern, often linked to elevated levels of DHT, a by-product of testosterone.
While this can be distressing, there are several effective treatments available, including DHT blockers like finasteride and natural remedies such as DHT-blocking shampoos and foods.
Understanding the root cause of hair loss, particularly the role of hormones, is crucial in selecting the right treatment. With the right approach, women can combat hair thinning and loss, promoting healthier and more robust hair growth.
As always, it's essential to consult with a medical professional before starting any treatment to ensure it's the best fit for individual needs.
FAQs
How can women reduce DHT?
Women can reduce DHT levels naturally by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, managing stress, ensuring adequate rest, and performing scalp massages to alleviate tension and boost blood circulation.
What are the symptoms of high DHT in females?
Symptoms of elevated DHT in females include increased growth of body, facial, and pubic hair (hirsutism), cessation of menstrual periods (amenorrhoea), heightened acne, and abnormal changes to the genitalia.
Which vitamin is a DHT blocker?
Biotin acts as a DHT blocker and is commonly found in supplements like gummies or pills. Foods rich in biotin include beef, bananas, broccoli, and sweet potatoes. Additionally, Vitamin B3 or Niacin promotes blood circulation to the scalp, supporting hair follicle health and blocking DHT.
How can I block DHT naturally?
To naturally block DHT, consume foods known to reduce DHT production. This includes foods high in zinc, lycopene, and lysine. Spinach, kale, pumpkin seeds, green tea, beetroot, banana, and flax seeds are among the top natural DHT-blocking foods.






